Actions in the field of climate neutrality result in an increased demand for green energy. Challenges are emerging in the form of the need to ensure balancing of the system with a significant share of distributed generation.
All these issues are the cornerstone of PSE Strategy for 2020-2030.
PSE’S STRATEGIC OBJECTIVES
-
Fending off external threats
- Management of the risk of loss of ability to control/manage the operation of the PPS, related to cyber-attacks against IT/OT systems of the transmission system operator and distribution system operators, generators, traders, exchanges or industrial consumers.
- Management of the risk of unavailability of infrastructure by developing cooperation with government administration in order to ensure joint and several responsibility for the physical security of the Company's facilities and for ensuring adequate measures to protect IT and technical resources, and protection from hostile actions.
Key initiatives executed under the strategy:
PSE CG Cybersecurity Programme Educational initiatives, events and actions promoting the security of critical power infrastructure -
Representing interests of the national electricity market
- Reducing tariff costs by decreasing unscheduled flows, achieved through coordination of the capacity calculation process, including the management of phase shifter settings and costly remedial actions such as redispatching, covering all PPS borders with the DA and ID Flow-Based Market Coupling mechanism.
- Management of the regulatory risk arising from the provisions of the “Clean Energy for All Europeans” package.
Key initiatives executed under the strategy:
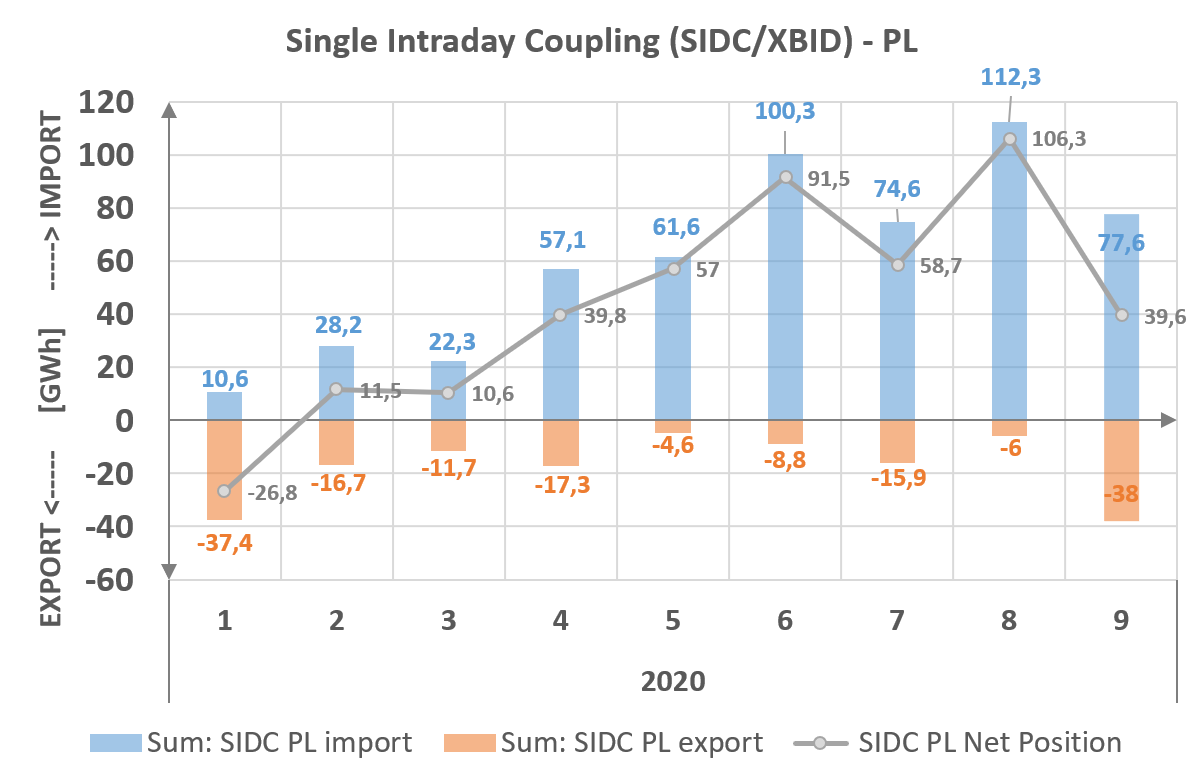
Development of the methodology for remedial actions related to capacity allocation and congestion management (CACM Article 35) and the methodology of cost sharing related to those actions (CACM Article 74) Development of the Concept Note containing key assumptions for the methodology under Article 76 of SO GL in the Core CCR Implementation of the Single Intraday Coupling mechanism on Polish borders Cooperation with government administration in the process of implementing the provisions of the Clean Energy Package for All Europeans package -
Security for future generations
- Long-term security of electricity supply. Implementing the capacity market and supporting tools.
- Pursuing the Strategy for Sustainable Development. Responsibility for the impact of the Company's operations on the national economy, natural environment and society.
Key initiatives executed under the strategy:
Capacity Market -
Responsible development
- Full network model with integrated acquisition of electricity and ancillary services as a basis for efficient electric power markets. Introduction of locational pricing as a mechanism that coordinates the functioning of generating and load resources and improving the quality of investment signals.
- Avoiding the transfer to future generations of the stranded costs of depreciation of assets that have lost their usefulness due to a change in the operation of the power system.
- PSE's care of public interests (system data and metering information).
- Innovations aimed at adjusting the system to a new shape of markets and new technologies (electromobility, multi-agent systems, local balancing zones, IoT, energy storage, distributed generation, and change of the energy mix).
- Facilities covering electricity demand in periods of insufficient generation at sources (electricity storage facilities or peak sources).
- Provision of the Polish Power System resources for electricity supply to consumers.
Key initiatives executed under the strategy:
Supporting the government administration in preparing legal arrangements concerning the Electricity Market Information Operator Development of the business process model of the electricity retail market for the purposes of the Central Electricity Market Information System Performing financial and optimisation feasibility analyses of the use of energy storage facilities Performing a feasibility analysis of the use of heuristic algorithms for scheduling outages of network elements in production run of medium-term coordination planning processes -
Stable operation of the system
- Operation continuity – planning, implementing, testing and improving procedures related to the Company's day-to-day operations.
- Improving, through the continuous improvement process, the transmission infrastructure operation model of the Polish Power System based on Predictive Maintenance (PdM) Techniques.
- Intervention DSR service.
Key initiatives executed under the strategy:
Approval of the updated Business Continuity Plan and update of the Business Continuity Management Book Development of DSR IP services and contracting reduction capacity Development and rollout of new functionalities of the IP-DSR system -
Money spent better
- Implementing investment projects and improving the New Investment Implementation Model.
- Improving the balancing market model.
- Automation of business processes.
Key initiatives executed under the strategy:
Conceptual work in designing new balancing market operation rules -
PSE resources
- Smart PSE.
- Adaptive capacity of the Company: know-how, structures and internal procedures prepared for quick legislative changes taking place in the energy market, and the technical and organisational requirements of new solutions.
- Human capital: employee development, competence management, job evaluation, strengthening the organisational culture based on responsibility and professionalism.
- PPS and energy market data.
- Finance transformation at PSE as a project aimed to streamline and modify the operation of the finance area at the Company.
- New Health Safety Environment Quality (HSEQ) management model.
Key initiatives executed under the strategy:
Improvement of the integrated environmental, health and safety management system
- Network Segmentation – in this area, projects are implemented which are aimed to ensure adequate separation of resources with different sensitivity levels; both through actions at infrastructure level and through appropriate design of business projects.
- Workstation – covers projects providing secure work tools, allowing performance and functionality to be maintained according to business needs, while ensuring protection from malicious software, and rights and data flow control.
- Internet Interface – functional and unified access to the Internet (including a secure Wi-Fi network deployed in 2017 at the company’s head office in Konstancin-Jeziorna) for the company’s employees and guests, and secure remote access adequate to needs.
- Detection and response – in order to ensure current ICT security, the dedicated Security Operations Centre (SOC) team performs the monitoring of threats on a 24-hour basis. In the case of incidents involving IT or OT networks, it takes relevant actions and remedial measures. The Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT) forms another line of support. CERT was set up in 2016, and in 2017 it became an accredited member of the Trusted Introducer organisation. It is involved in enhancing employees’ awareness through the publication of threat alerts and warnings, publication of ICT security bulletins and reporting information on incidents. It is also engaged in cooperation with third parties in incident handling coordination and exchange of information on threats with third parties (e.g. CERT NASK, Government Security Centre, cert.gov.pl).
- Digital Committee Cyber Security Task Force – a team responsible ENTSO-E’s cybersecurity strategy, headed by the director of PSE’s ICT Department;
- Critical System Protection (CSP) – the group deals with the protection of critical infrastructure;
- Cyber Security Special Interest Group – the group deals with ICT security issues. Its task is to monitor information on global threats, cooperate under projects where care of security is required, and shape the rules for secure operation of systems and operators.
- ENTSO-E’s Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) Working Group – a group that has prepared electronic information standards in the European electricity market.
 GRI 103-1 GRI 103-2
GRI 103-1 GRI 103-2
Educational initiatives, events and actions promoting the security of critical power infrastructure
- In January 2019, on PSE’s initiative, the Council of Ministers adopted the Regulation amending the Regulation on facilities of particular importance for the security and defence of the state and their special protection (Journal of Laws of 2003, No 116, item 1090, as amended). In the new regulation, “load dispatch centres and electrical substations of strategic significance for the national power system” were recognised as Category I facilities of particular importance for the security and defence of the state.
- In September 2019, PSE, in coordination with Tauron Polska Energia, hosted the first conference for experts and individuals responsible for ensuring the security of critical power infrastructure. The Security of Power Facilities conference brought together more than 80 representatives of power companies, the Ministry of Energy, the Internal Security Agency, the General Police Headquarters and voivodeship Police headquarters, the General Fifer Service Headquarters, as well as representatives of Security and Crisis Management Departments of voivodeship authorities.
- In September 2019, we co-hosted the 3rd SAFE PLACE National Scientific Technical Congress “Anti-terrorist Security of Public Utility Buildings”. The subjects of the congress included the issues of anti-terrorist protection of facilities critical to national security and unprotected buildings, anti-terrorist education, and the issue of public resilience against terrorism. PSE representatives participated in workshops and discussions during expert panels.
- In November 2019, PSE hosted the participants of the 7th Congress of Postgraduate Studies for the Police Academy students majoring in Strategic Management of Internal Security of the State. The lectures discussed the issues of counteracting terrorist hazards to facilities of strategic significance for the state. The practical component included operational demonstrations by the National Power Dispatch Centre (PSE), the National Gas Dispatch Division (Gaz-System), and the Liquid Fuel Depot in Emilianów (PERN).
- In December 2019, we co-hosted the 7th Congress of Postgraduate Studies for the Police Academy students majoring in Strategic Management of Internal Security of the State. The lectures discussed the roles and tasks of critical infrastructure owners and related legislative changes. The event provided an opportunity for the exchange of views and experience sharing, and to discuss relevant security issues related to facilities of critical importance for the state.

 GRI 103-1 GRI 103-2
GRI 103-1 GRI 103-2
Development of the methodology for remedial actions related to capacity allocation and congestion management (CACM Article 35) and the methodology of cost sharing related to those actions (CACM Article 74)
- cost sharing covers exclusively the cost of eliminating overloads on cross-border relevant network elements (interconnectors and internal elements with PTDF>5 percent),
- cost sharing covers exclusively the cost of remedial actions ordered (energy only, without the capacity component),
- the implementation is dependent on other methodologies (the capacity calculation methodology, the methodology under CACM Article 74 and SOGL Article 76), and the deployment of IT tools.
- the cost sharing process requires: the identification of flows by category (loop flows, internal flows, import/export flows, transit flows and PST flows), the mapping of the costs of remedial actions onto other elements (total cost split between specific lines), and calculation of the aggregate cost to be covered by the country (bidding zone) concerned,
- the methodology does not prejudge the sequence cost assignment to particular flow categories or details of mapping, decomposition, etc.,
- the cost of eliminating overloads on network elements other than cross-border relevant are covered by the element owner,
- the cost on uncoordinated remedial actions are covered by initiators of uncoordinated actions,
- TSOs have the right to use PTS to reduce loop flows,
- the costs generated by non-Core countries are to be identified, but covered by Core operators.
 GRI 103-1 GRI 103-2
GRI 103-1 GRI 103-2
Development of the Concept Note containing key assumptions for the methodology under Article 76 of SO GL in the Core CCR.
- the principle of avoiding the aggravation of the situation on selected (observed) elements outside the region,
- the method of determining cross-border impact remedial actions, i.e. remedial actions subject to coordination,
- definition of information on remedial actions which has to be exchanged between TSOs and RSCs,
- designation of the hours for performing security analyses in intraday processes (00:00, 08:00, 16:00), with the option to add a fourth hour (fixed or on-demand),
- determination of the basic rules for the operation of the remedial action optimiser (RAO),
- providing preliminary assumptions on the method of activation and rejection of remedial actions and the initial description the fast activation process.
 GRI 103-1
GRI 103-3
GRI 103-1
GRI 103-3
Cooperation with government administration in the process of implementing the provisions of the Clean Energy Package for All Europeans package

 GRI 103-1
GRI 103-1
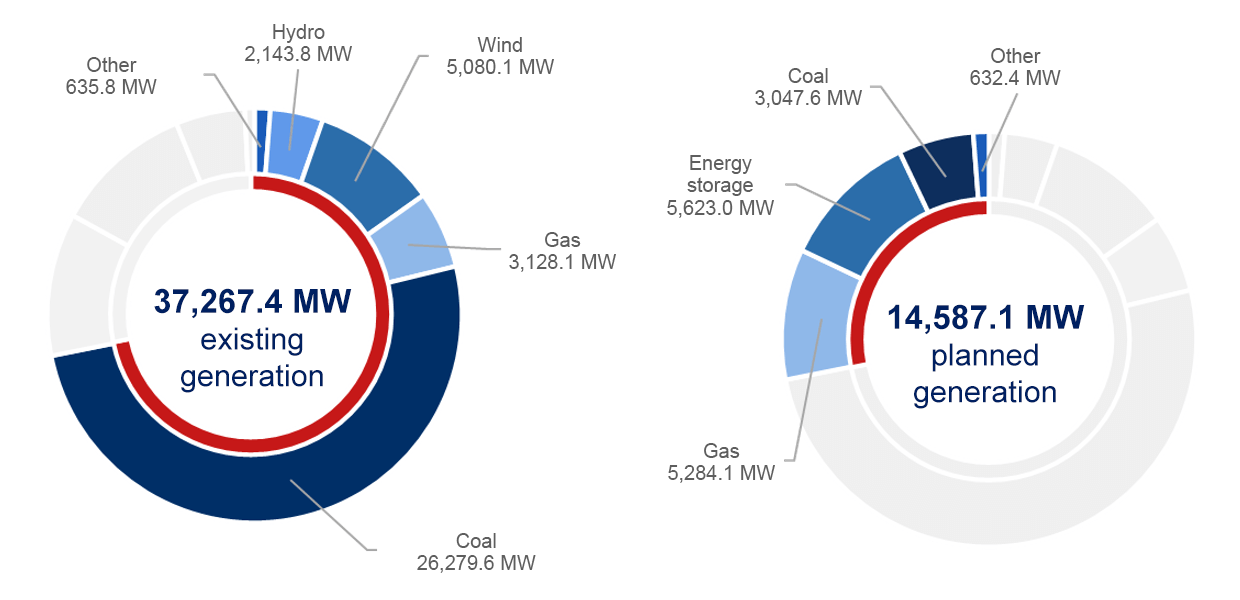
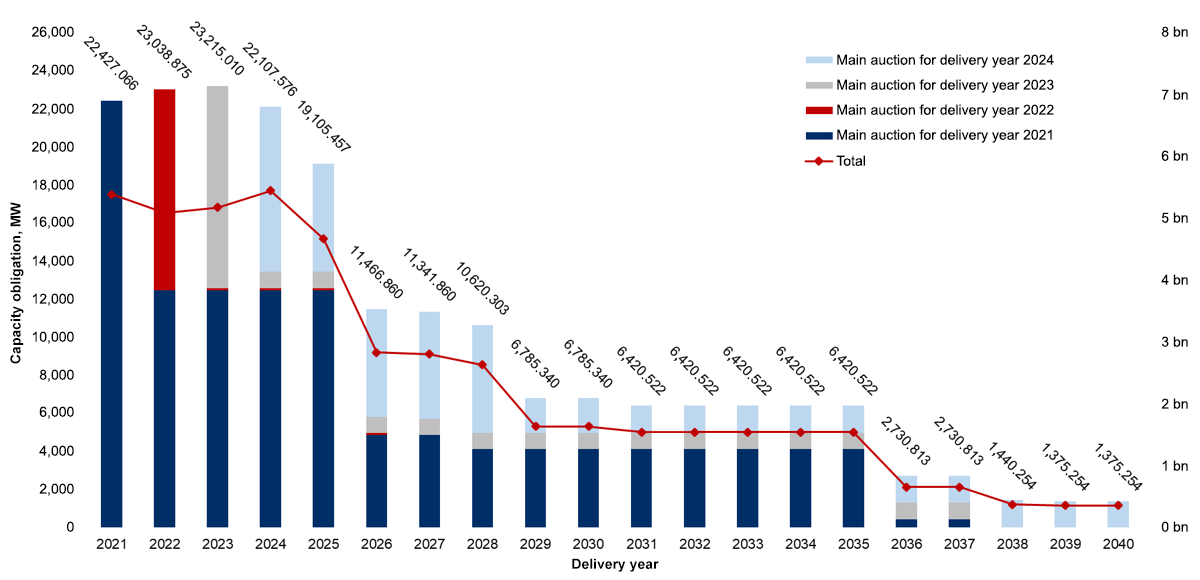
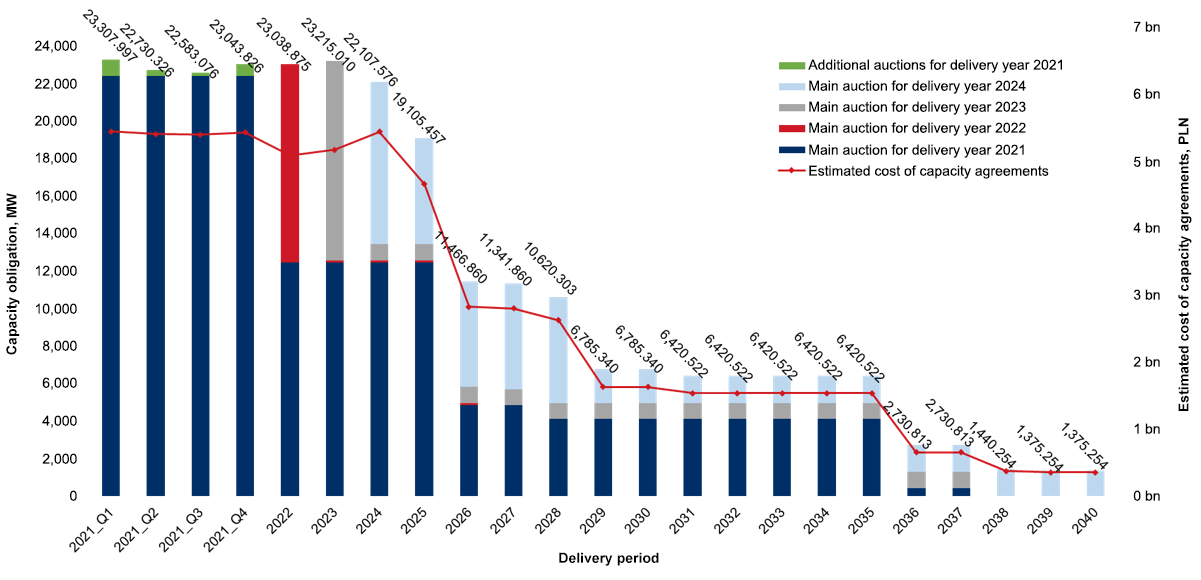
Capacity Market
| - | Number of units entered in the register | Total net maximum capacity of units entered in the register, MW |
|---|---|---|
| Existing generating physical units | 900 | 37,267.446 |
| Planned generating physical units | 85 | 14,587.115 |
| Demand side response physical units | 36 | 413.190 |
| Demand side response physical units | 71 | 2,120.000 |
| Total | 1092 | 54,387.751 |
| Delivery year | Auction closing price PLN/kW/year | Number of capacity agreements concluded | Capacity obligation volume resulting from capacity agreements concluded (MW) | Auction closing round |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2024 | 259.87 | 103 | 8,671.154 | 5. |
| Duration of the capacity obligation in years | Number of agreements concluded in main auction for delivery year 2024 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 71 |
| 2 | 1 |
| 5 | 15 |
| 7 | 12 |
| 15 | 1 |
| 17 | 3 |
| Total capacity agreements concluded | 103 |
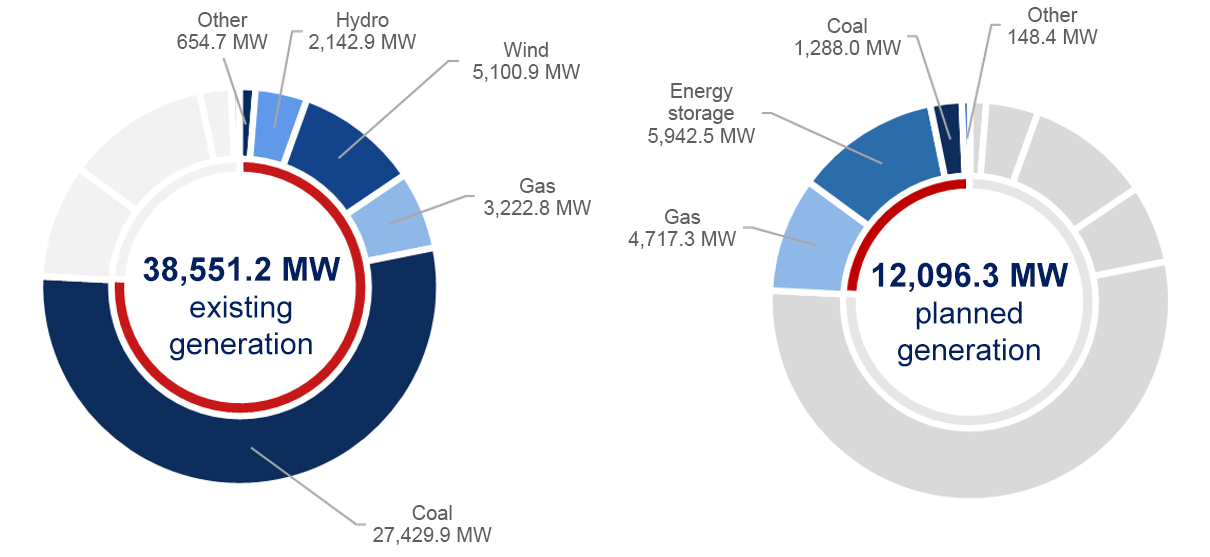
| - | Number of units entered in the register | Total net maximum capacity of units entered in the register, MW |
|---|---|---|
| Existing generating physical units | 920 | 38,551.128 |
| Planned generating physical units | 99 | 12,096.266 |
| Demand side response physical units | 60 | 527.565 |
| Planned demand side response units | 109 | 3,681.000 |
| Total | 1188 | 54,855.959 |
| Quarter of 2021 | Auction closing price (PLN/kW/year) | Number of capacity agreements concluded | Capacity obligation volume resulting from capacity agreements (MW) | Auction closing round |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | 286.01 | 25 | 880.931 | 1. |
| II | 286.01 | 7 | 303.260 | 1. |
| III | 286.01 | 5 | 156.010 | 1. |
| IV | 286.01 | 17 | 616.760 | 1. |
- continuation of the monitoring of capacity agreements concluded,
- management of transactions concluded in the secondary market, including the reallocation of the capacity obligation,
- replacement of planned demand side response units,
- performing tests of demand side response units,
- implementation of mechanisms supporting the participation of foreign capacity in the Capacity Market,
- collection of the capacity fee,
- integration with metering/billing data acquisition systems,
- verification of the performance of the capacity obligation,
- implementation of the Capacity Market settlement model.

Supporting the government administration in preparing legal arrangements concerning the Electricity Market Information Operator

Development of the business process model of the electricity retail market for the purposes of the Central Electricity Market Information System

Performing financial and optimisation feasibility analyses of the use of energy storage facilities
In the event a storage facility performs market functions (price arbitrage by third parties), our company may not be an owner and operator of such facilities. It is legally permissible for such operations to be performed by an SPV subsidiary belonging to the PSE Group, taking into account the rules of unbundling (legal ban on combining electricity transmission or distribution with electricity trading or generation, mainly to prevent the formation of monopolies to the disadvantage of final consumers). In such a case, the operations of the storage facility would have to be profitable to an extent enabling the SPV to be self-sustainable, as it is not possible to include related investment and operating costs in the tariff.

Performing a feasibility analysis of the use of heuristic algorithms for scheduling outages of network elements in production run of medium-term coordination planning processes
 GRI 103-1
GRI 103-1
Approval of the updated Business Continuity Plan and update of the Business Continuity Management Book
- 6 contracts in the winter package for the period from 1 January 2019 to 31 March 2019 with a guaranteed capacity volume of 510 to 535 MW in individual hours,
- 10 contracts in the summer package for the period from 1 April 2019 to 30 June 2019 with a guaranteed capacity volume of 362.5 to 534,5 MW in individual hours (with the option to obtain a maximum of 609,5 MW by shifting flexible products).
- GP V Package No 1L (PPS excluding 5 areas from GP IV Areas ) – service provision period from 1 April to 30 September 2020 – expected capacity of 715 MW, contract awarded on 17 December 2019, with 683.7 to 764.5 MW of guaranteed capacity acquired;
- GP V Package No 1Z (covering the entire PPS) – service provision period from 1 February to 31 March 2020 and from 1 October to 30 November 2020 – expected capacity of 600 MW, contract awarded on 17 December 2019, with 612 MW of guaranteed capacity acquired;
- GP IV covering packages 2L÷6L, i.e. 5 packages corresponding to dedicated areas (Poznań, PAK, Łódź, Lublin-Zamość, Zielona Góra) – service provision period from 1 April to 30 September 2020 – the contract was awarded on 25 October 2019, with 25.5 MW of guaranteed capacity acquired;
- CP with the service provision period from 1 January to 31 December 2020. Contracts under the tendering procedure were awarded on 26 September 2019 – the service will be provided by four companies: Enspirion Sp. z o.o., Enel X Polska Sp. z o.o., Tauron Polska Energia S.A. and Lerta Sp. z o.o.;
- PBU with the service provision period from 1 January to 31 December 2020. Contracts under the tendering procedure were awarded on 26 September 2019 – the service will be provided by four companies: Enspirion Sp. z o.o., Enel X Polska Sp. z o.o., Tauron Polska Energia S.A. and Lerta Sp. z o.o.

Conceptual work in designing new balancing market operation rules
- acquisition of balancing energy and balancing capacity based on market mechanisms;
- integration of the national balancing market with the European platforms for the exchange of balancing energy;
- creation of price signals reflecting the balancing situation in the PPS and providing a basis for taking correct (from the point of view of the effectiveness of the whole sector) modernisation decisions.

Improvement of the integrated environmental, health and safety management system
